Brand Speak
Samsung’s Journey
Published
4 years agoon
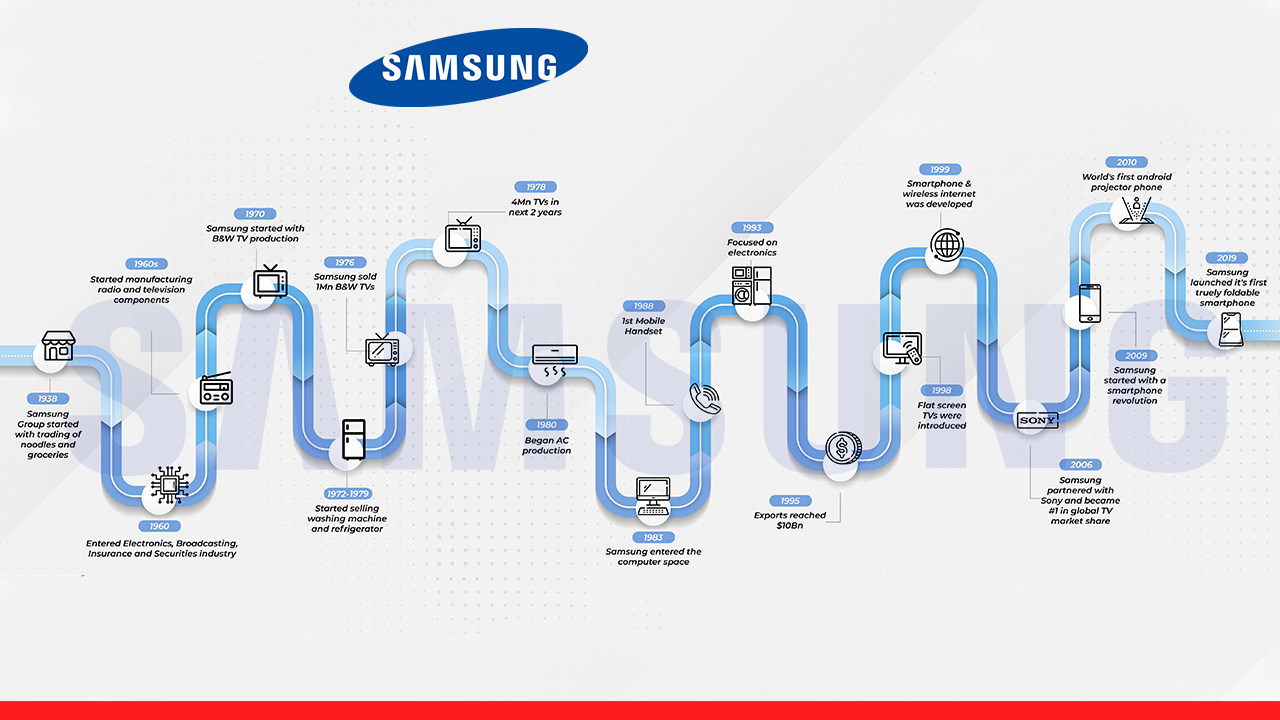
Lee Byung-chul (1910-1987), who belonged to a wealthy territory family in the Uiryeong area, constructed Samsung after moving to the adjacent city of Daegu in 1938.
Samsung was founded in Su-dong as a modest business with 40 representatives. It was in charge of making dried fish, essential products, and noodles. As soon as the Korean War began, Lee had to flee Seoul. In 1954, Lee established Cheil Mojik. There was the biggest woolen manufacturing plant in the country.

Samsung expanded its worldwide influence. Lee had to make Samsung a leader in several industries. In 1947, Lee Byung-Chul, the creator of Samsung, and another company called Samsung Mulsan Gongsa, or the Samsung Trading Corporation, received financial support from Cho Hong-Jai, the coordinator of the Hyosung social affair.
The commerce firm changed into the present-day Samsung C&T Corporation. After only a few years of operation, Cho and Lee fell over different management styles. After purchasing the Gumi-based Hanguk Jeonja Tongsin in 1980, Samsung entered the broadcast communications industry. Back then, it had switchboards for sale.
Samsung found the hardware business in the 1960s, but the following construction experiences occurred in the 1970s. They divided the Samsung Group into the Shinsegae Group, CJ Group, and Hansol Group following Lee’s destruction in 1987.
In the first quarter of 2010, Samsung Electronics overtook Nokia, the market leader since 1998, in terms of unit sales, to become the largest PDA maker worldwide. Samsung Electronics, Samsung Heavy Industries, Samsung Engineers, and Samsung C&T are just a few well-known Samsung auxiliary businesses today.
Some well-known auxiliary businesses are Samsung Life Insurance, Samsung Consumers Can Also Benefit, and Cheil Worldwide. Samsung impacts South Korea’s media, culture, governance, and economic growth. Samsung had a critical element in the Supernatural incident on the Han River.
The auxiliary institutions of South Korea create around one-fifth of the country’s finished commodities. The $1,082 billion GDP of South Korea made up exactly 17% of Samsung’s income.
Samsung received U.S. licenses in 2015, compared to companies like IBM, Google, Sony, Microsoft, and Apple. Samsung acquired 7,679 utility licenses as of December 11, 2015. On August 19, the day after the launch of the Note7 in August, it went on sale.
Beginning in September 2016, it discontinued selling phones due to several device issues. Samsung stopped selling phones and investigated its stock.
Some phone models’ batteries had a distortion that allowed them to release excessive heat, causing fires and crashes, which is how this incident occurred. Samsung substituted a different model for the assessed phones. It was later found that the updated interpretation.
Subsequently, it was discovered that the Galaxy Note 7’s updated model also had a similar battery distortion. On October 10, 2016, Samsung completed a comprehensive examination of all Galaxy Note7 PDAs. At the same time, it also completed the production forever.
Which types of business strategies are used for growing Samsung’s income organization?
The Samsung marketing strategy was one of the best since it assisted a corporation with a focus on costs in changing its direction and becoming a power producer. In this way, Samsung likewise anticipated change to access the strategic position, and the new Samsung showing approach was the key to progress.
Due to consumers’ constantly shifting desires in the industry, they expected associations to move quickly and provide their customers with dynamic and propelled products.
Over a long period, Samsung has built exceptional business processes. Samsung was not well, but it was now neither too long ago. Samsung has made such strides in recent years that it is now the principal competitor of Apple Company.
Samsung is now the top tech business by revenue and the seventh-largest brand in the world. The way Samsung presented its products pushed them to become a major factor in the industry’s expansion.
In addition to its products, they acclaimed Samsung for its customer service. However, the most important component of Samsung’s expanding mix is its thin assortment. Discounting Price Samsung uses cost-cutting measures like Apple to gain the upper hand over its rivals.

For instance, the Galaxy S6 and S6 Edge are the faultless results of Samsung assuring that the greatest cell phone manufacturer ever manufactured and promoting the brand “Next is Now.”
Price Centering Samsung has trouble gaining a competitive advantage over its rivals in several areas. Samsung is a respectable brand. However, it cannot compete with Google in terms of household appliances, particularly cameras and other equipment. Samsung can’t compete with Canon and Nikon.
In clear urban networks, Samsung has a partnership with a single dispersion business that distributes the items uniformly over the city. For instance, it’s astonishing how Samsung uses one association to distribute its products in Mumbai.
How does Samsung Rides high in the Indian economy?
Samsung Electronics, led by TV manufacturer Samsung Electronics, is by far the greatest CEO in the cell phone industry. India’s most recognized and adaptive brand is Samsung. It is the designer of the greatest and best 4G data network on the planet Reliance Jio.
Perceptions, marketing battles, openings, and rivalry occasionally from long-distance rivals, nearby upstarts, and emerging Chinese brands annoy Samsung. In any event, Samsung has always had the option to avoid danger and maintain its position.
After it pulled down Nokia in 2012, it dominated the market in the flexible industry and the TV segment for more than 12 years. Utilizing a Smartphone, as seen by some verifiable analysis of companies tracking phone sales, Chinese company Xiaomi is inching closer to or has perhaps surpassed Samsung after the third quarter of 2017.
While Samsung controlled the cell market for the entirety of 2017, statistics showed Xiaomi led the last quarter with a 26.8 percent share of the overall market. Samsung’s percentage was 24.2%. Different players, such as Vivo, Lenovo, and Oppo, separately maintained 6.5, 5.6, and 4.9 percent of the market.
Warsi, who has been employed by Samsung for up to 12 years and has advanced to the position of Global Vice President, is brave. These difficulties provide the chance to work harder for customers and accessories.
According to an anonymous industry official, India should be Samsung’s most important market by a wide margin. The current plan is to evolve into a more profitable wireless industry.
According to sources, Samsung India earned a mind-boggling INR 34,300 crores from cell deals in 2018–19. That is an increase of 27% and more than $5.5 billion. The biggest rivals of Samsung are talking about living off of $1 billion to $2 billion in India.
According to revenue, Samsung is the top producer of consumer hardware worldwide. In terms of revenue, Samsung Electronics has been the world’s second-largest innovation organization since roughly 2019. Its market capitalization has maintained at US$301.65 billion, making it the 18th-largest planet.
Samsung offers an example and is the leader in the sector. It invested heavily in India, in which there were 22 years of economic relationships and significant stakes in surrounding undertakings. It employs more than 10,000 plan engineers at research facilities around India, making it may be the best scout among the IITs.
In February, Samsung’s actions and the productive product launch of leads like the Galaxy S8, Note8, Galaxy S9, and S9+ propelled in February, safeguarded the trouble and raised the brand’s profile as a reliable association.
Consider India In the months leading up to the summer of 2015, Samsung’s make for India framework, which aligns with the company’s skill India initiative, was considered.
India is important for Samsung since it is the second-largest phone market in the world today and maybe the best-untapped market for some high-end devices. Surprisingly few appliances like refrigerators, clothes washers, microwaves, and limited air systems are introduced due to factors such as continuous electricity availability, societal influence, lifestyle, and profit.
Even with Chinese companies making real inroads into the Indian PDA market, the definitive pay for the Korean powerhouse increased by 15.5 percent to INR 55,511.9 crore in FY 2017 from INR 48,053 crore the same year.
This pay increase included turnover and other compensation, which increased by the same amount, or INR 15,511.93 crore, to INR 55,511.9 crore in FY 2017. Samsung maintained its market lead, while the association’s TV business remained weak at INR 4,481.2 crore.
Samsung claimed in its papers that the “Make for India” program, through which a significant portion of the products was planned and manufactured to meet the needs of Indian customers, had been a tremendous success and a major factor in the sequence of events.
Every department at Samsung India operated at full capacity, with the TV business increasing and the home appliance business increasing. The mobile phone industry was the biggest supporter of gross advantage, contributing INR 5,005.9 crore, or 44 percent, in FY17.
What kind of plans does Samsung have?
According to two top industry chairmen, Samsung has planned a new project worth around INR 2,500 crore to transform its operations in India into a hub for the components industry.
Although developed, even more efforts already exist. For the world of smartphones, phones, and batteries, the Korean organization has established two new components manufacturing facilities in India Samsung Display Company and Samsung Electronics India.
Samsung Venture Investment Corporation, the company’s finance division, has independently set up initiatives in India to support start-up companies in the hardware and software industries.
Two very different Samsung India and other wireless carriers who now source components from Samsung’s overseas missions will receive supplies from the component associations.
The executives claim that Samsung Electronics intends to contribute an additional INR 900–1,000 crore and would finalize the plans after working with the Centre following the general elections.
These suppositions follow the introduction of the world’s largest mobile phone manufacturing facility in India a year earlier at a full-scale cost of INR 4,915 crore. Normal completion is anticipated for 2020.
You may like
-


The India EU trade deal will make your dream cars cheaper, but not today
-


Union Budget 2026: Auto sector seeks traction on input costs
-


Union Budget 2026: India’s infrastructure leaders outline their expectations
-


Union Budget 2026: Healthcare leaders hoping for a shot in the arm
-


Union Budget 2026: AI firms outline their key expectations.
-


NSDC International Enabling Opportunities for Indian Youth to Japan After Japanese Language Training, Strengthening India–Japan Skilled Mobility Corridor


